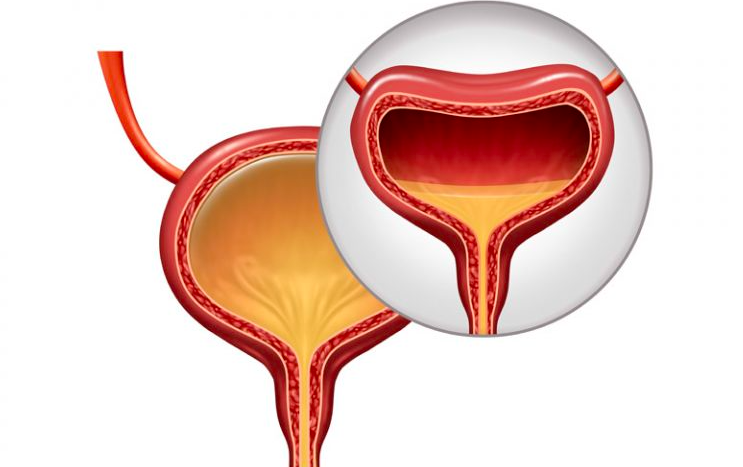
Impacts on the body if urination is retained for a long time.

Retaining urine for a long time can have various consequences on the body, and it is generally not recommended. Here are some potential issues that may arise:
Bladder Distension:

Is frequent urination a sign of bad disease?
Bladder distension refers to the stretching and enlargement of the bladder beyond its normal capacity. When urination is retained for a prolonged period, the bladder continues to fill, and its walls expand to accommodate the increasing volume of urine. This distension can have a few results on the bladder's design and capability. Here are some key points:
Decreased Bladder Muscle Tone:
Over time, the continuous stretching of the bladder can lead to a decrease in muscle tone. This might bring about debilitated withdrawals during peeing and add to troubles in discharging the bladder.
Reduced Bladder Sensation:
Chronic bladder distension can affect the nerves that signal when the bladder is full. The bladder may become less sensitive to the need to urinate, leading to delayed or weakened signals to empty the bladder.
Impaired Bladder Function:
Bladder distension can contribute to dysfunction in the coordination between the detrusor muscle (responsible for contraction) and the sphincter muscles (responsible for controlling the release of urination). This might prompt issues like an overactive bladder or urinary maintenance.
Increased Risk of UTIs:
An enlarged bladder gives a stale pool of microbes to duplicate, expanding the gamble of urinary parcel diseases (UTIs). UTIs can cause discomfort, and pain, and may lead to more serious complications if not treated promptly.
Potential for Permanent Damage:
If bladder distension is severe and prolonged, it may result in irreversible damage to the bladder walls and nerves. This can affect generally speaking bladder capability and may require clinical mediation.
Summary:
It's essential to resolve issues connected with pee maintenance speedily and look for clinical consideration assuming that you experience constant hardships with pee. Chronic bladder distension is a sign that the normal urinary system function is compromised, and healthcare professionals can provide appropriate evaluation and treatment options based on the underlying causes.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs):

How Turmeric Prevents Heart Attack/Cancer?
When urine is retained for a long time, it can increase the risk of developing urinary tract infections (UTIs). Urination serves as a medium for bacterial growth, and when it is held in the bladder for extended periods, bacteria have more time to multiply, leading to infection. Here are some ways in which urine retention can contribute to UTIs:
Stagnant Urination:
Retained urination becomes stagnant in the bladder, providing a conducive environment for bacteria to proliferate. Bacteria, most commonly Escherichia coli (E. coli), can ascend from the urethra into the bladder and multiply in the stagnant urination.
Incomplete Emptying:
If the bladder is not fully emptied during urination due to retention issues, residual urine may contain bacteria. This residual urination can act as a reservoir for bacteria, increasing the likelihood of infection.
Compromised Immune Defense:
The normal flushing action of urine helps remove bacteria from the urinary tract. When urination is retained, this flushing action is impaired, allowing bacteria to adhere to the bladder walls and multiply. The immune defenses in the urinary tract may also be compromised, making it easier for bacteria to cause an infection.
Urethral Contamination:
Stagnant urination in the bladder can lead to contamination of the urethra, the tube that carries urination from the bladder to the outside of the body. Bacteria can enter the urethra more easily and migrate upward to the bladder.
Symptoms of a UTI may include:
- Pain or burning during urination
- Frequent and urgent need to urinate
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urination
- Lower abdominal pain or discomfort
- Fever and chills (in more severe cases)
Summary:
If you suspect a UTI or experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention promptly. UTIs can be treated with antibiotics, and early intervention can prevent the infection from spreading to the kidneys or other parts of the urinary tract. Chronic or recurrent UTIs may require further investigation and management by a healthcare professional.
Bladder Dysfunction:

Bladder dysfunction can occur as a result of retaining urination for a long time, and it involves impaired coordination and function of the bladder muscles. Prolonged urine retention can negatively impact the normal contractile abilities of the bladder and may lead to various issues related to its function. Here are some aspects of bladder dysfunction associated with urination retention:
Decreased Bladder Muscle Tone:
Continuous stretching of the bladder due to urine retention can result in a decrease in muscle tone. The detrusor muscle, responsible for contracting and emptying the bladder, may become weakened over time.
Incomplete Emptying:
If the bladder is not able to contract effectively, it may not fully empty during urination. Residual urine can remain in the bladder, contributing to a cycle of incomplete emptying and further complications.
Overactive Bladder:
Bladder dysfunction may manifest as an overactive bladder, where there is a sudden and involuntary contraction of the bladder muscles. This can lead to a frequent and urgent need to urinate, even when the bladder is not full.
Urinary Retention:
While urinary retention is often a cause of bladder dysfunction, it can also be a consequence. The bladder may struggle to expel urination efficiently, leading to incomplete voiding and increased residual urination.
Impaired Nerve Function:
Bladder dysfunction may involve impaired nerve signals between the brain and the bladder muscles. This disruption in communication can affect the coordination needed for proper bladder function.
Increased Risk of Infections:
As mentioned earlier, stagnant urination in the bladder can increase the risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs). Infections can further exacerbate bladder dysfunction and contribute to additional complications.
Summary:
Bladder dysfunction can significantly impact an individual's quality of life, causing symptoms such as urgency, frequency, incontinence, and discomfort. If you are experiencing difficulties with urine or suspect bladder dysfunction, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional. They can conduct a thorough evaluation, which may include imaging studies, urodynamic testing, and other diagnostic measures to determine the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment options.
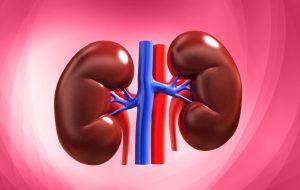
Kidney Damage:
Sweaty hands? – What is the solution?
Retaining urination for a long time can potentially lead to kidney damage. The kidneys assume a significant part in sifting side effects and an overabundance of liquids from the blood to shape pee. When urination is not expelled from the body regularly, it can have several implications for kidney health:
Backflow of Urination:
Retaining urination can lead to a backflow of urine into the ureters, which are the tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder. This condition is known as vesicoureteral reflux. The discharge of pee can open the kidneys to expanded pressure and the gamble of disease.
Hydronephrosis:
Prolonged urination retention can result in the accumulation of urine within the kidneys, causing them to become swollen. This condition is called hydronephrosis and is characterized by the dilation of the renal pelvis and calyces due to the backup of urination.
Increased Pressure:
Stagnant urination in the bladder can lead to increased pressure in the urinary tract, affecting the normal functioning of the kidneys. Elevated pressure within the urinary system may compromise the kidneys' ability to filter blood and produce urination.
Risk of Infections:
Urination in the bladder for an extended period provides a favorable environment for bacterial growth. Infections in the urinary tract can potentially ascend to the kidneys, causing pyelonephritis—a serious kidney infection.
Renal Dysfunction:
Chronic exposure to increased pressure and the risk of infection can contribute to renal dysfunction over time. Kidney capability might be debilitated, affecting the capacity to control electrolytes, liquids, and side effects in the body.
Summary:
It's important to note that severe or chronic kidney damage can have serious health consequences and may require medical intervention. On the off chance that you experience steady troubles with peeing, lower stomach torment, or different side effects demonstrative of kidney issues, looking for brief clinical attention is vital. A medical care professional can direct demonstrative tests, for example, imaging review and kidney capability tests, to survey the degree of any potential kidney harm and decide on proper therapy choices. Early intercession is fundamental to forestall further intricacies and protect kidney capability
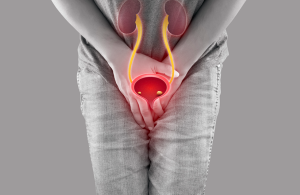
Incontinence:
What happens to the lungs after smoking and what happens to the body from the moment you quit?
Retaining urination for a long time can contribute to urinary incontinence, a condition where there is an involuntary loss of urine. Several mechanisms can lead to incontinence in individuals who have been retaining urination for extended periods:
Pelvic Floor Weakening:
Chronic retention of urination can put increased pressure on the pelvic floor muscles, leading to weakness over time. The pelvic floor muscles assume a significant part in supporting the bladder and controlling the arrival of pee. Weakened pelvic floor muscles can result in stress urinary incontinence, where urine leaks during activities such as coughing, sneezing, or laughing.
Bladder Stretching:
The bladder can become distended and stretched if urination is held for too long. Prolonged stretching of the bladder can affect its muscle tone and elasticity. As a result, the bladder may not contract effectively, leading to difficulty in controlling the release of urination.
Detrusor Muscle Dysfunction:
The detrusor muscle is responsible for contracting and emptying the bladder. Chronic retention of urine can lead to dysfunction in the detrusor muscle, affecting its ability to contract properly. This brokenness might add to overactive bladder side effects, including desperation and urge incontinence.
Neurological Implications:
Prolonged urination retention may impact the nerves that control bladder function. Nerve harm or brokenness can upset the correspondence between the bladder and the mind, prompting disabled coordination and command over the bladder.
Summary:
It's essential to recognize that incontinence is a symptom that can result from various underlying causes. If someone is experiencing incontinence or has concerns about their urinary health, consulting with a healthcare professional is advisable. A medical services supplier can lead an intensive assessment to recognize the particular elements adding to incontinence and suggest proper therapy choices, including way-of-life changes, pelvic floor activities, prescriptions, or careful mediation, contingent upon the fundamental reason.
Increased Risk of Kidney Stones:

How do painkillers damages the kidneys?
Retaining urination for an extended period can increase the risk of developing kidney stones. Kidney stones are hard stores that structure in the kidneys when there is an irregularity of substances that make up pee, like calcium, oxalate, and phosphorus. Several factors associated with urine retention can contribute to the formation of kidney stones:
Concentration of Minerals:
When urination is held in the bladder for too long, water is reabsorbed, and the remaining urination becomes more concentrated. Concentrated urine is more likely to contain higher levels of minerals and salts, increasing the risk of crystal formation in the kidneys.
Stagnant Urination:
Prolonged urination retention provides a stagnant environment in the bladder. In stagnant urine, minerals and salts may precipitate and form crystals. These gems can then total and form into kidney stones.
Decreased Flushing Action:
Normal urination helps flush out minerals and waste products from the kidneys. When urination is retained, the flushing action is compromised, allowing minerals to accumulate and form stones.
Increased Risk of Infections:
Stagnant urination can also promote the growth of bacteria in the urinary tract. Diseases can prompt the creation of substances that energize stone arrangement, adding to the advancement of kidney stones.
Urethral Contamination:
Stagnant urination in the bladder can lead to contamination of the urethra, allowing bacteria to enter the urinary tract more easily. This can add to the development of struvite stones, which are related to particular sorts of bacterial diseases.
Summary:
It's important to note that kidney stones can be painful and may cause symptoms such as severe flank pain, blood in the urination, and urinary urgency. Assuming that somebody is encountering side effects reminiscent of kidney stones or has worries about their urinary well-being, it is critical to look for clinical consideration. A medical care proficient can perform demonstrative tests, like imaging review and pee investigation, to distinguish the presence of kidney stones and suggest proper administration, which might incorporate way of life changes, drugs, or techniques to eliminate or separate the stones.
Hypertrophy of the Bladder Wall:

Keep these eight things in mind to avoid kidney disease or problems.
Hypertrophy of the bladder wall refers to an increase in the thickness and muscularity of the bladder's muscular layer, known as the detrusor muscle. This condition can occur as a consequence of chronic bladder distension and urine retention for a long time. Here are some aspects of hypertrophy of the bladder wall associated with prolonged urination retention:
Adaptive Response:
The detrusor muscle of the bladder is responsible for contracting during urination to expel urine. When the bladder is consistently stretched and distended due to urination retention, the detrusor muscle may undergo hypertrophy as an adaptive response to the increased workload.
Loss of Elasticity:
Chronic stretching of the bladder wall can lead to a loss of elasticity and compliance. The bladder may become less able to contract effectively, resulting in difficulties in emptying during urination.
Reduced Contractile Efficiency:
Hypertrophy of the bladder wall can affect the contractile efficiency of the detrusor muscle. The increased muscle mass may not necessarily translate into improved function, and the bladder may experience impaired contractility.
Contributing to Bladder Dysfunction:
Hypertrophy, along with changes in bladder compliance and contractility, can contribute to overall bladder dysfunction. This dysfunction may manifest as issues with emptying the bladder, increased residual urine, and potential complications such as an overactive bladder.
https://livewithgreen.com/urination-retained-for-a-long-time-impacts/
.jpg)